LIOR SKOURY

ES System
The system was built as a plug-in for Grasshopper and supports the new construction method developed by INDAN LTD. The method combines light gauge steel design with concrete castings, enabling the construction of strong structures in a short time frame and without the skilled manpower, such as in the assembling of IKEA furniture.
Based on the understanding that the planning stage can create a bottleneck in the production chain, the customer asked to produce software that would "know" how to take the 2D architectural drawing, together with the engineering drawing, and from them to create a 3D model using the new method that contains all of the information needed for production, from the blue prints to the machine G-code.
The system has three stages:
Preliminary analysis of the structure and all of its intersections.
Detailing of the initial analysis according to the construction details of the method.
Production of the various panels according to the details and accumulation of the information required for each.
The system was made using Python with the Grasshopper library in Rhino and the Shapely library outside of Rhino.
The project was created at ParaGroup-Israel LTD.
Client: INDAN LTD.
Year: 2018
Team: Lior Skoury, Shahar Abelson
Role: Team leader and developer
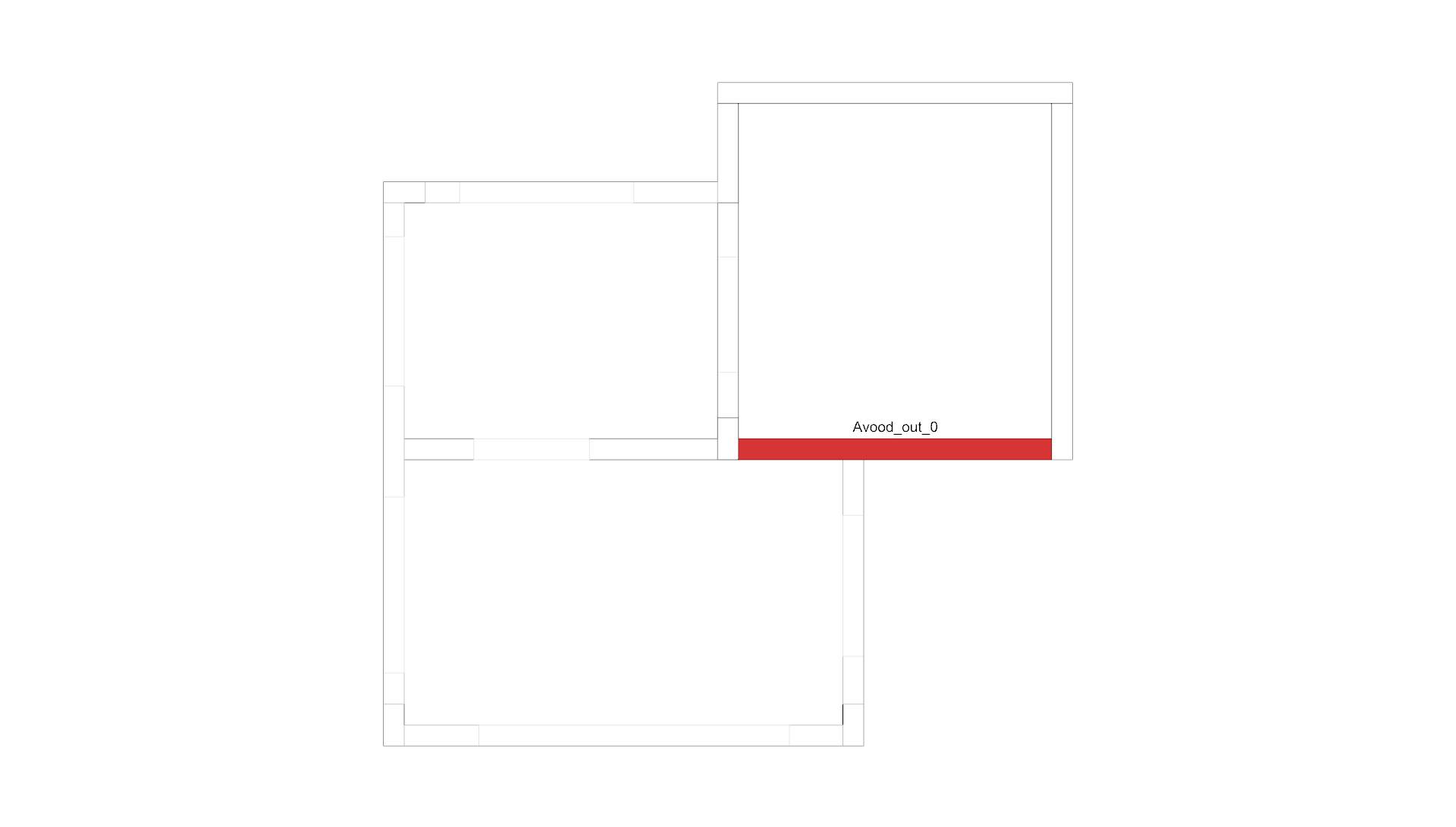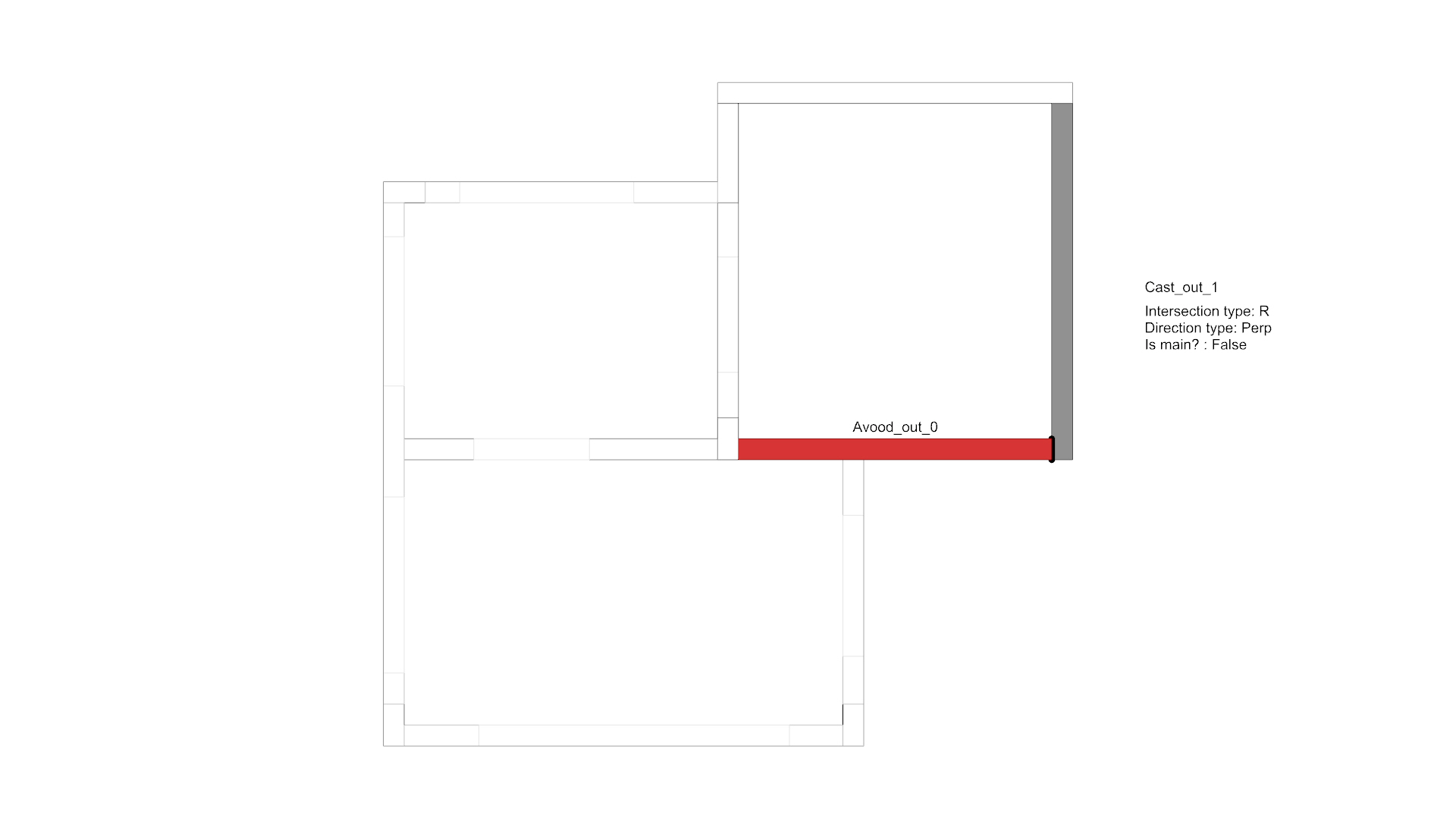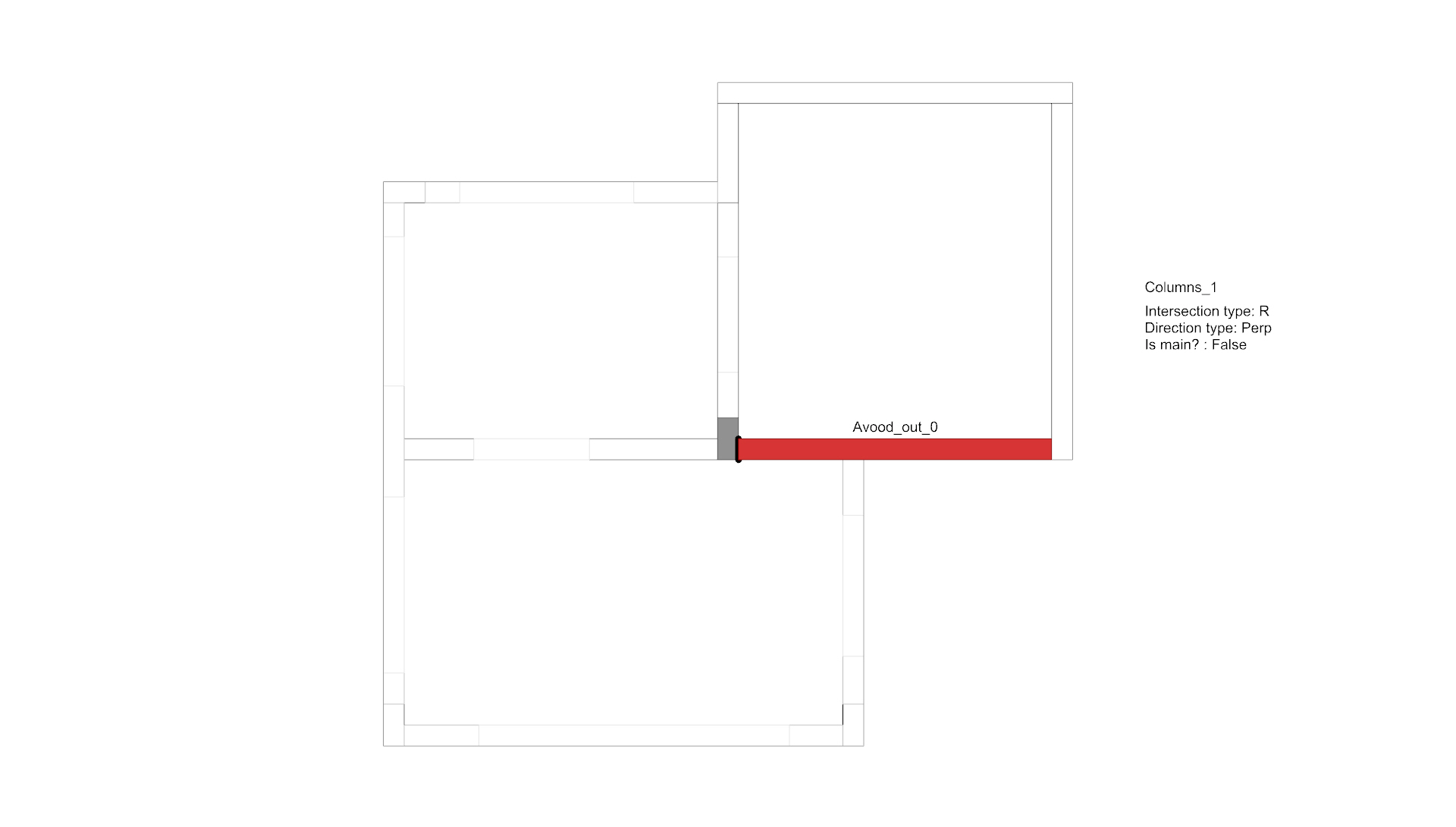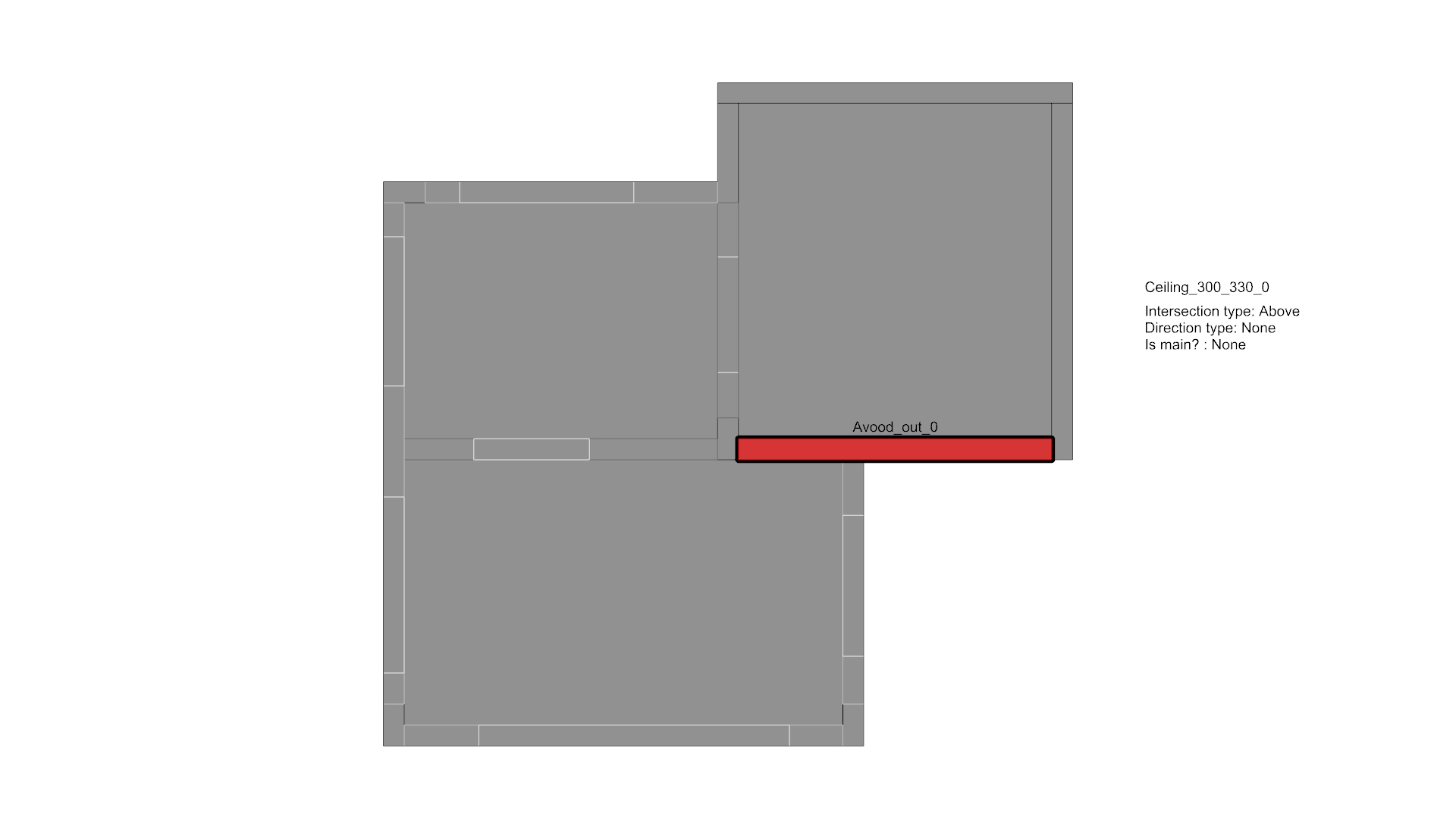

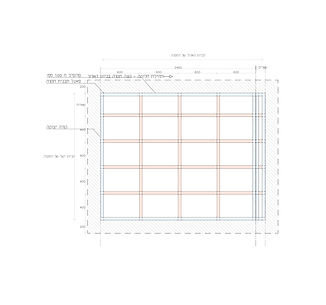
An example of an element in a structure that is analyzed, with all of its intersections counted and aggregated.
The process repeats itself in every element in the structure.
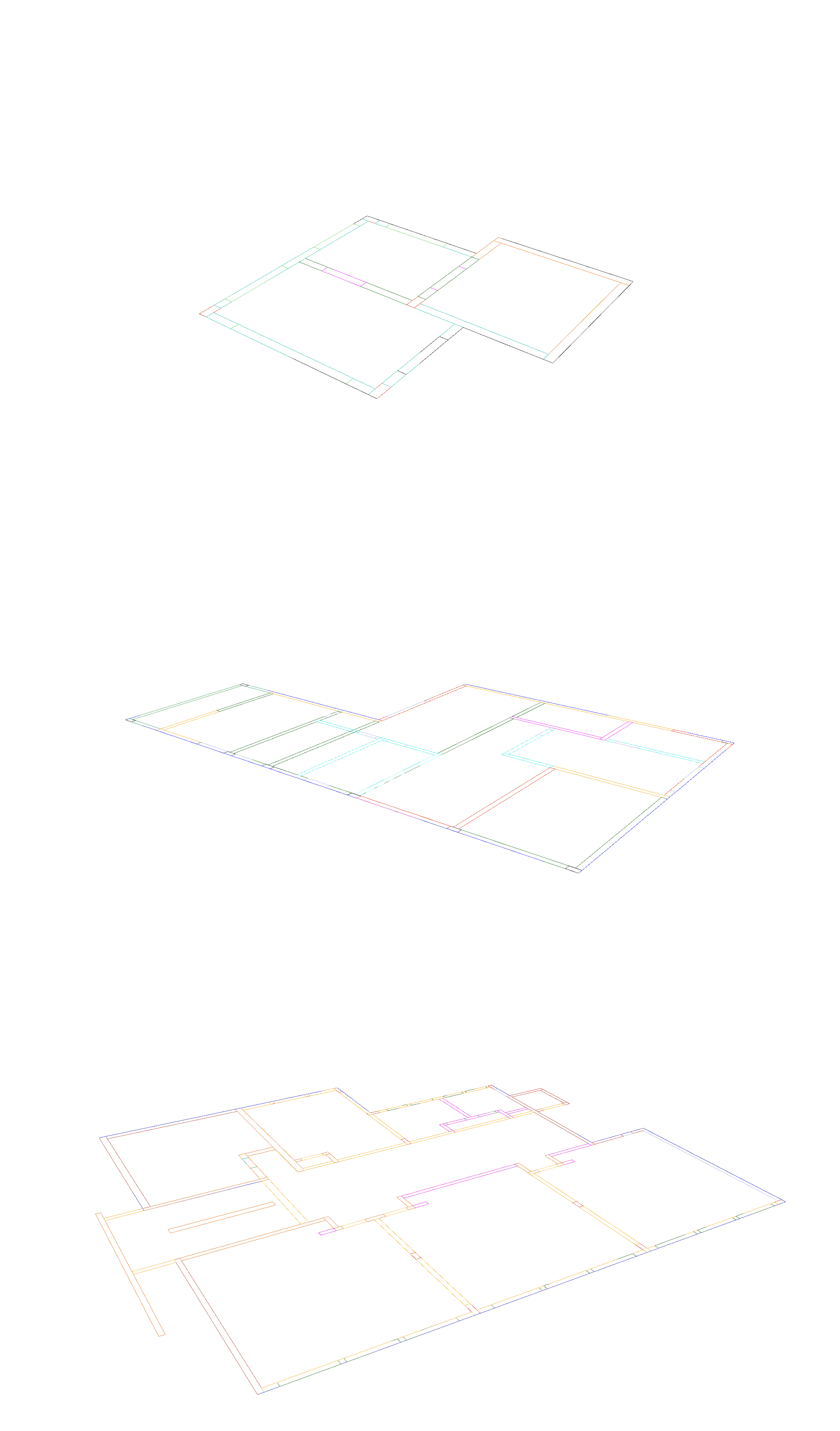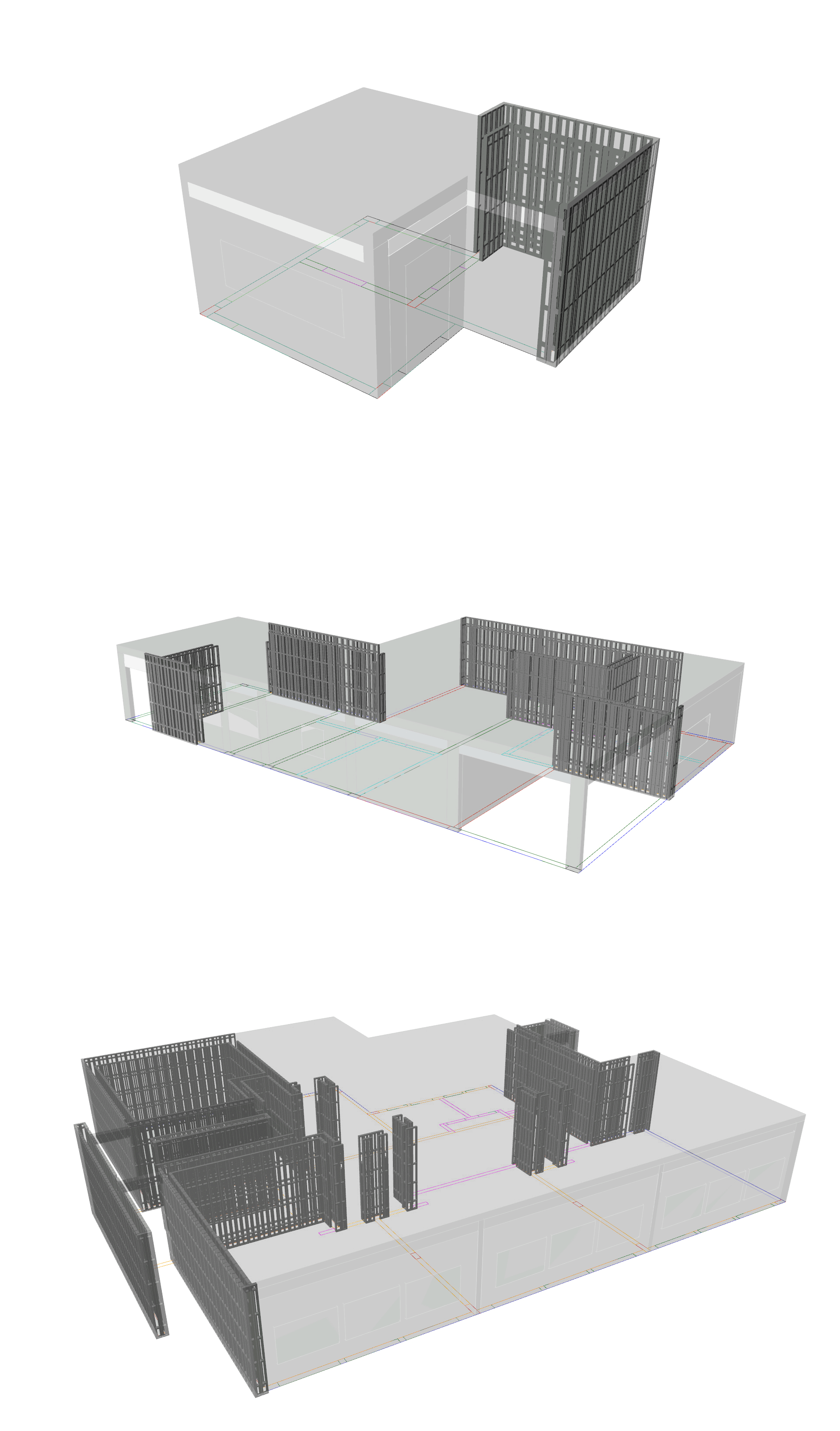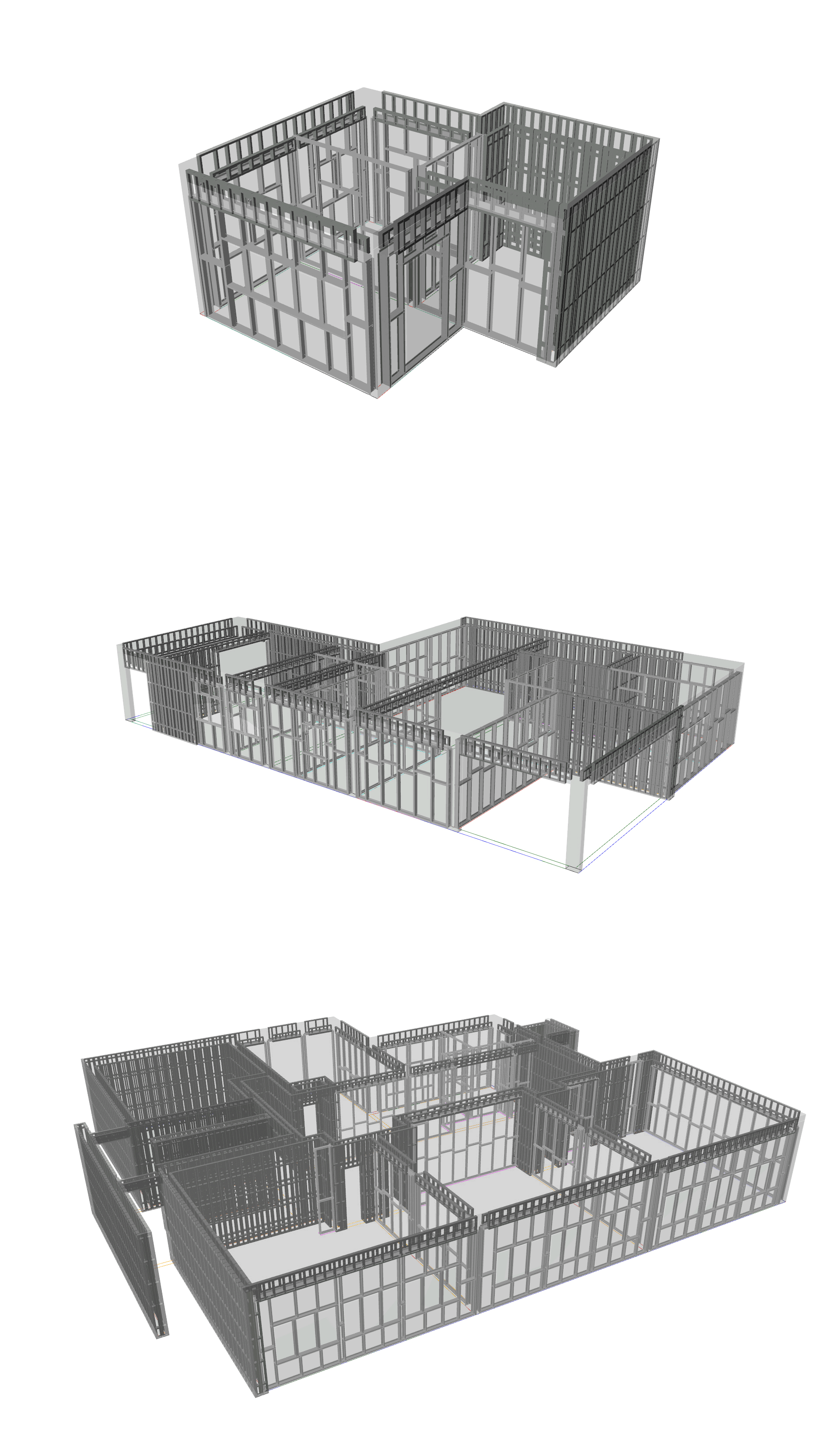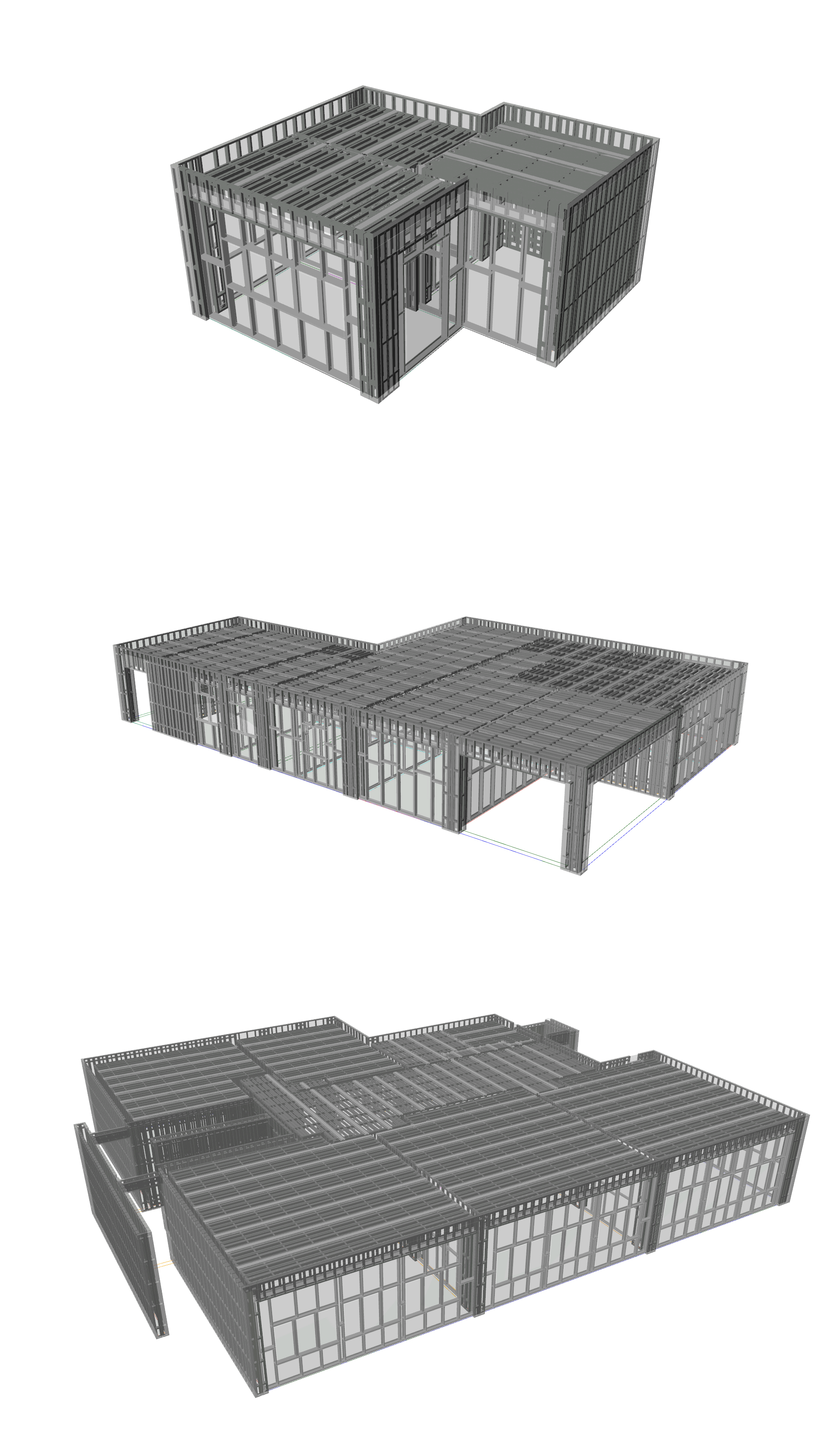
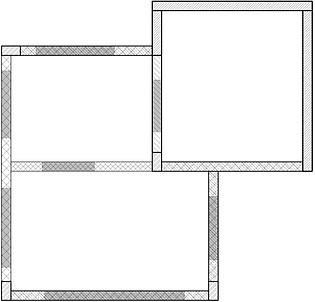
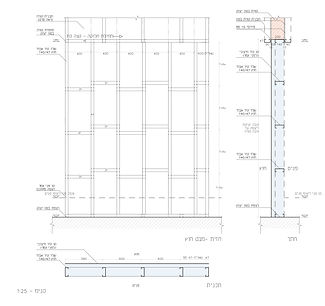
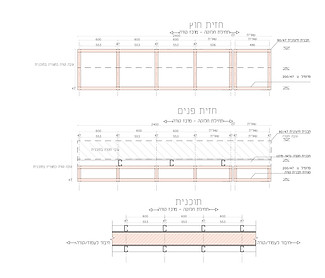
Typical 2D input with detailing layers and heights



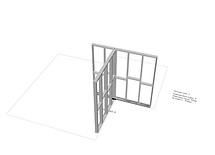




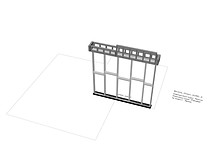



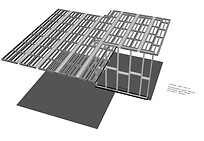
Each intersection is unique, and its construction is done in accordance with the method details. In the event that the cross-sections converge on each other, it is necessary to understand the correct intersection according to the details.
There are more than 150 details in each method, and each corresponds to a different intersection.
Cast Walls Out

Regular Walls Out
Beams
Cast Walls In

Regular Walls In

Ceilings
Apart from the details of the intersections, each element has a different construction method that is appropriate to the way it is applied in the overall structure.